Table of Contents
As electric vehicles (EVs) rapidly gain traction worldwide, with sales exceeding 10 million units in 2023 and still indicating a significant increase by 2030, the importance of choosing the right EV adapter has never been more critical. In a landscape marked by a diverse array of charging stations and EV models, choosing an adapter that ensures compatibility, safety, and optimal charging is crucial. Every EV model comes with specific charging requirements and connector types, making compatibility a primary consideration in adapter choice. Safety and performance also play vital roles. High-quality adapters should meet stringent safety standards, and be capable of handling your EV’s maximum charging rate to avoid extended charging times. In the following sections, we’ll explore the nuances of EV adapters, and the global landscape of charging connectors, and guide you in choosing the right adapter for your EV, ensuring a seamless and efficient charging experience.
1. What is an EV Adapter?
EV adapters play a pivotal role in this ecosystem, serving as a crucial link between different charging infrastructures and EVs. An EV adapter is essentially a device that allows an electric vehicle to connect to a charging station with a different connector type than the one the vehicle is designed for. It acts as a bridge, enabling compatibility between the vehicle’s charging port and the charging station’s plug.
2. Global EV Charging Connector Landscape Overview
The landscape of Electric Vehicle (EV) charging connectors mirrors the diversity of the global EV market. To navigate this complex terrain, we will delve into the distinct methods of EV charging—namely Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)—and provide a comprehensive overview of the various global EV charging connectors, highlighting their unique characteristics and functionalities.
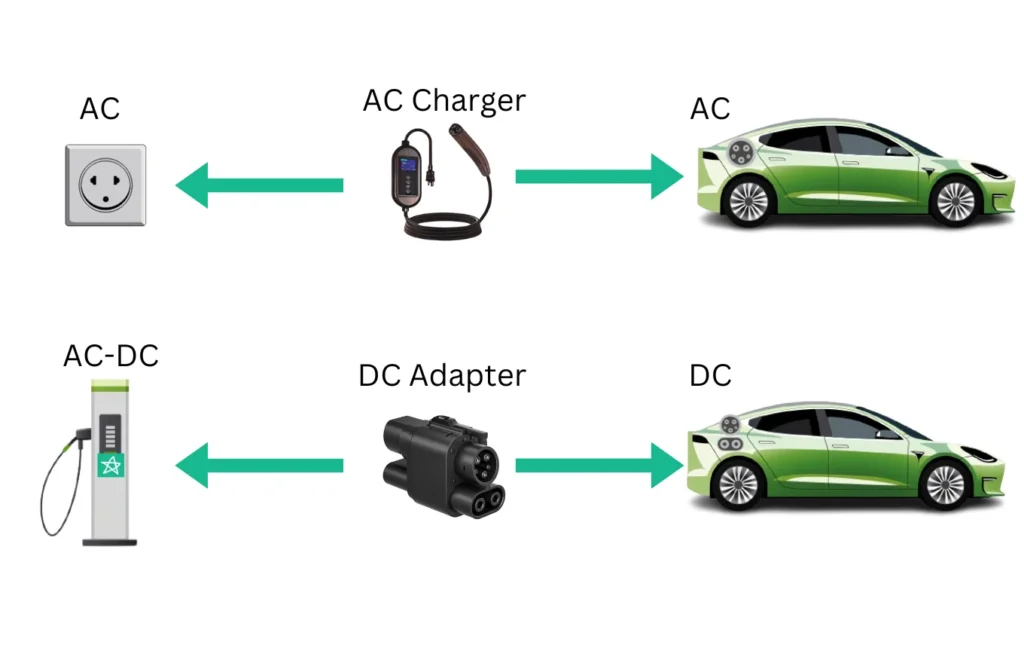
2.1 AC vs. DC Charging in EVs
- AC (Alternating Current) Charging: AC charging is the most common form of EV charging, typically used for daily, residential, and workplace charging. EVs equipped with an onboard charger convert AC from the grid to DC for battery storage. AC chargers are categorized into Level 1 and Level 2, with Level 1 offering up to 2.4 kW (using standard household outlets) and Level 2 providing up to 22 kW (requiring specialized equipment). The choice of an adapter for AC charging largely depends on matching the connector type of the vehicle to the charging station.
- DC (Direct Current) Charging: DC charging, often referred to as fast or rapid charging, is primarily used in commercial and public charging stations for quick top-ups. These chargers directly feed DC power to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger, and offering much higher charging speeds, typically ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW. Adapters for DC charging need to support high power throughput and ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s fast-charging protocol.
2.2: Types and Features of EV Charging Connectors
Below is a professional overview of the major global EV connectors, categorized by their compatibility with AC and DC charging methods. This information is vital for understanding the diverse landscape of EV charging technology.
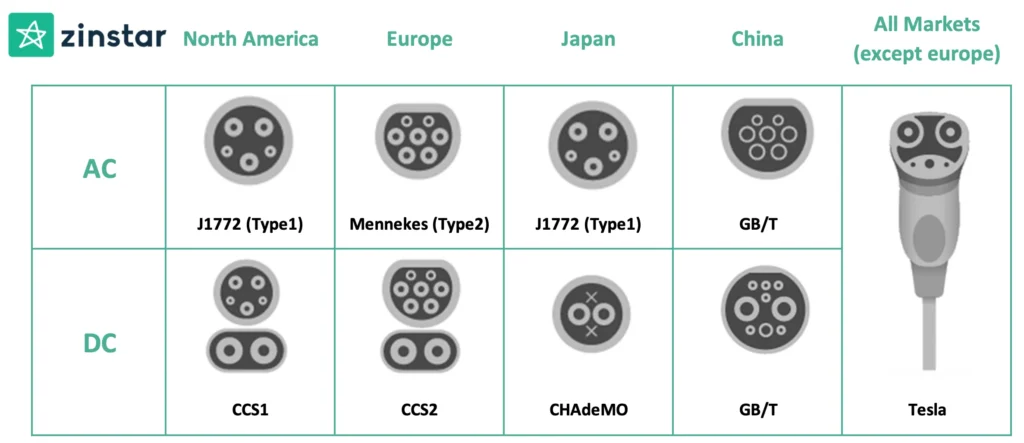
Further delve into the distinct characteristics of key EV charging connectors such as Type 1, Type 2, GB/T, CCS1, CHAdeMO, CCS2, and Tesla, will examine each connector’s unique features and specifications in the electric vehicle industry.
| Picture | Connector Type | Typical Power Capabilities | AC or DC Charging | EV Charging Levels | Technical Features |
 | J1772 (Type 1) | Up to 7.4 kW | AC | Level 1, 2 | 5-pin design with grounding, locking mechanism |
 | Mennekes (Type 2) | Up to 43 kW | AC | Level 1, 2 | 7-pin design, compatible with single and three-phase power |
 | GB/T AC | Varies | AC | Level 1, 2, 3 | Chinese standard, varies with specific model |
 | CCS1 | Over 350 kW for DC | DC | Level 3 | Combo connector with Type 1 for AC, additional DC pins |
 | CCS2 | Over 350 kW for DC | DC | Level 3 | Combo connector with Type 2 for AC, additional DC pins |
 | CHAdeMO | Up to 100 kW | DC | Level 3 | Large connector, secure locking, supports bidirectional charging |
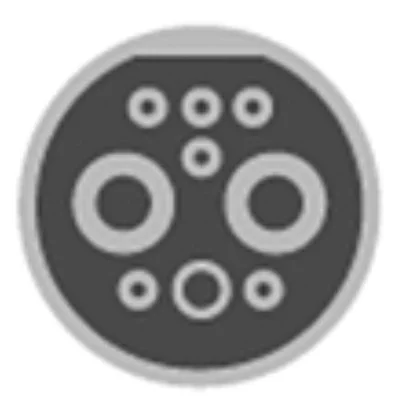 | GB/T DC | Up to 250 kW for DC | DC | Level 3 | Chinese standard for DC charging, high power capability |
 | Tesla | Up to 250 kW | AC/DC | Level 1, 2, 3 | Compact design, high-speed charging, exclusive for Tesla Superchargers |
3: How to Select the Appropriate EV Adapter
Selecting the right EV adapter for your vehicle is a crucial step in ensuring efficient and reliable charging. A straightforward approach to this selection process lies within the naming conventions of the adapters themselves, typically formatted as “Charger Station to EVs.” This naming rule can greatly simplify finding a compatible adapter for your electric vehicle.
For example, if you own a Tesla vehicle with its proprietary connector and are looking to charge at a station equipped with a J1772 (Type 1) plug, you would seek an adapter named “J1772 to Tesla EV adapter” or related Tesla EV adapters. This designation clearly indicates that the adapter will connect a J1772 charger to a Tesla vehicle port. It’s crucial to first determine the type of connector your Tesla uses and then match it to the J1772 connector found at many charging stations. This ensures that you select an adapter that provides not only the physical connection but also compatibility with the charging infrastructure you intend to use.
While this rule provides a quick and easy method to identify the right adapter, it’s also important to consider other factors such as the adapter’s power handling capacity, safety certifications, and build quality. Ensuring these aspects align with your vehicle’s requirements and safety standards will guarantee a safe and efficient charging experience.
4: Frequently Asked Questions and Answers about EV Adapters and EV connector types.
Question: What are the different types of EV plugs?
Answer: The main types of EV plugs (charging connectors) include:
- J1772 (Type1): Common in North America and parts of Asia for AC charging.
- Mennekes (Type 2) : Widely used in Europe for AC charging.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): A combination of Type 1 or Type 2 with two additional DC pins for fast charging, prevalent in North America (CCS1) and Europe (CCS2).
- CHAdeMO: A DC fast charging standard originating from Japan.
- Tesla Connector: Tesla’s proprietary connector used in their vehicles.
- GB/T: China’s standard connector for both AC and DC charging.
Question: What are the different types of electric car charging adapters?
Answer: Electric car charging adapters vary based on the connector types they bridge. A straightforward approach to this selection process lies within the naming conventions of the adapters themselves, typically formatted as “Charger Station to EVs”. Common EV adapter types include:
- J1772 (Type 1) to Tesla EV Adapter- Used to connect a Tesla vehicle to a J1772 (Type 1) charging station.
- Tesla to J1772 (Type 1) EV Adapter- Allows non-Tesla vehicles with a J1772 inlet to charge at a Tesla destination charger.
- CHAdeMO to CCS1 EV Adapter- Enables a vehicle with a CCS1 inlet to use CHAdeMO charging stations.
- Type 2 (Mennekes) to Type 1 (J1772) EV Adapter- Used for charging a Type 1 EV at a Type 2 charging station, common in Europe.
- Type 1 (J1772) to Type 2 (Mennekes) EV Adapter-Allows a Type 2 EV to be charged at a Type 1 charging station, often used in North America.
- CCS1 to CCS2 EV Adapter-Facilitates charging a CCS2 vehicle at a CCS1 charging station, bridging the North American and European CCS standards.
- GB/T to Type 2 (Mennekes) EV Adapter-Enables vehicles with a Type 2 inlet to use GB/T (Chinese standard) charging stations.
- Type 2 (Mennekes) to Tesla EV Adapter-Used for charging a Tesla vehicle at a Type 2 charging station.
Question: Is J1772 and CCS the same?
Answer: No, J1772 (or Type 1) and CCS are not the same. J1772 refers to a specific type of connector used primarily for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging. CCS (Combined Charging System), on the other hand, includes the J1772 connector for AC charging but adds two additional pins for DC fast charging. CCS is a more versatile connector supporting both AC and DC charging.
Question: What is the difference between a Type 1 and Type 2 EV charging cable?
Answer:The primary difference between Type 1 and Type 2 EV charging cables is their design and regional usage. Type 1 cables, with a single-phase plug, are commonly used in North America and parts of Asia and support up to 7.4 kW. Type 2 cables are prevalent in Europe, can handle single or three-phase power, and support up to 43 kW for AC charging. The physical design and pin configuration of these two types are also different.
Question:Do all EVs use the same charging plug?
Answer: No, all EVs do not use the same charging plug. Different regions and vehicle manufacturers adopt various standards, leading to a variety of charging plugs in the market. Common types include Type 1, Type 2, CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla’s proprietary connector, and GB/T in China. The choice of plug often depends on the geographical location and the vehicle’s make and model.
Question: What is the difference between Level 2 and Level 3 EV chargers?
Answer: Level 2 and Level 3 EV chargers differ primarily in their charging speed and power output.
Level 2 Chargers: These are AC chargers that typically provide power ranging from 3 kW to 22 kW. They are commonly used for home and public charging and can fully charge an EV overnight or in a few hours.
Level 3 Chargers (also known as DC Fast Chargers): These chargers use DC power and offer much higher power levels, usually starting at 50 kW and going up to 350 kW or more. They are designed for rapid charging and can charge an EV to 80% in as little as 20-30 minutes. Level 3 chargers are typically found in commercial or public charging stations.








